The SaaS cloud computing market will grow from $273.55 billion in 2023 to $908.21 billion by 2030.
These numbers show an impressive 18.7% compound annual growth rate. Cloud adoption has leaped ahead by about five years since the pandemic started.
Most businesses share your interest in cloud solutions. The numbers tell the story – 87% of businesses operate with a multi-cloud strategy and 72% use hybrid cloud approaches. Public cloud usage alone has grown by 40% in the past year.
Businesses make this fundamental change because cloud computing cuts IT costs by 15-30%. Moving your business to the cloud without proper planning can create problems.
This piece explains cloud computing basics, different types available, and steps for smooth migration. You’ll learn the advantages of cloud computing and avoid common mistakes that affect many businesses.
Want to improve your operations without the stress? Let’s take a closer look.
What Is Cloud Computing and Why It Matters in 2025
Image Source: MDPI
Cloud computing has changed how businesses operate in the digital world. This technology has grown from a simple IT solution into a key business driver in 2025. Global spending on cloud services will reach $678 billion this year. Learning about cloud computing and its value has never been more significant.
Understanding the cloud computing definition
Cloud computing delivers computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—through the internet. Companies no longer need to buy, own, and maintain physical servers and data centers.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology states that cloud computing has five key characteristics:
- On-demand self-service: You can provision resources automatically without human interaction
- Broad network access: Resources are available over the network through standard mechanisms
- Resource pooling: Provider’s resources serve multiple customers using a multi-tenant model
- Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can scale quickly outward and inward based on need
- Measured service: Resource usage is monitored, controlled, and reported transparently
Cloud computing lets you access technology services when needed, instead of investing in and managing your own infrastructure.
Why is cloud computing important for modern businesses
Modern businesses can’t operate without cloud computing in 2025. Several compelling reasons explain this trend.
Cloud computing turns fixed expenses into variable costs. You pay only for what you use instead of investing heavily in physical infrastructure. This move from capital expenditure to operational expenditure creates greater financial flexibility.
Your business can adjust resources quickly based on need without buying new hardware. E-commerce platforms can handle 5-10 times normal volume instantly during high-traffic periods like Black Friday.
Security has improved dramatically. Cloud providers now offer protection that this is a big deal as it means that what companies can implement themselves. This solves one of the main concerns about cloud adoption.
Cloud computing makes innovation possible at scale. McKinsey predicts cloud computing will generate $3 trillion in global value by 2030. The value from innovation will be worth five times more than simple cost reduction.
Businesses know cloud computing will play a significant role in their success over the next five years. The technology creates foundations that speed up the adoption of other innovations like artificial intelligence and quantum computing.
Cloud computing examples in daily operations
Cloud computing powers many everyday business applications. Here are real-life examples:
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers applications through the internet, which removes installation and maintenance needs. Examples include:
- G Suite for document creation and collaboration
- Salesforce for customer relationship management
- MYOB for accounting
- Zoom for video conferencing
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources. Organizations use AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform to run applications without managing physical servers.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers development environments to build and deploy applications. AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Google App Engine are prime examples.
Industry-specific cloud platforms have gained most important traction in 2025. Organizations now use these specialized solutions to speed up their business initiatives. These platforms address unique industry needs rather than applying generic solutions.
Cloud computing has transformed remote work capabilities. Teams can access business systems from anywhere with an internet connection through cloud-based applications. This improves collaboration and increases efficiency.
Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
Image Source: MIT
Your business success depends on choosing the right cloud deployment model. Each model provides benefits that align with specific operational needs and budget constraints.
Public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud explained
The public cloud delivers computing resources over the internet by third-party providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. You share hardware with other companies but access only your data. This model changes upfront capital expenses into operational costs, so you pay only for what you use. Public clouds excel when workloads spike and need 1000 times more capacity during peak periods.
A private cloud creates a single-tenant environment dedicated to your organization. You control security, customization, and resource management better. Private clouds suit businesses with strict regulatory compliance needs or sensitive data concerns. Higher costs and maintenance responsibilities come as tradeoffs.
A hybrid cloud merges public and private environments into a unified infrastructure. You can keep sensitive data in private settings while using public clouds for expandable, non-critical operations. Hybrid cloud lets you “burst” into public cloud resources during traffic spikes without affecting private workloads.
The multi-cloud model uses services from multiple cloud providers at once. Unlike hybrid clouds that combine private and public resources, multi-cloud focuses on using different public clouds together. Your reliability increases since two cloud services rarely experience outages simultaneously.
Hybrid cloud computing for small business use cases
Small businesses choose hybrid cloud solutions more often now. This model gives cost flexibility by keeping predictable workloads in private settings while variable needs scale in public clouds.
Hybrid cloud works well for seasonal businesses. You avoid paying for idle infrastructure during slow periods yet scale up instantly during busy seasons. Research shows SMBs can reduce operational costs by a lot through hybrid setups as multiple companies share infrastructure expenses.
Security needs often push small businesses toward hybrid approaches. Customer data stays safe in private environments with custom security while customer-facing applications run in public clouds. This strategy creates layered protection against cyber threats.
Hybrid models help businesses transition smoothly to the cloud. Teams can move workloads gradually without disrupting operations while developing cloud expertise.
Cloud computing architecture basics
Cloud architecture shows how technology components work together to create computing environments. Front-end and back-end elements connect through networks.
The front-end represents what users see and work with—usually applications and interfaces accessed through web browsers. Users interact with the cloud through this graphical interface.
The back-end runs all behind-the-scenes operations with storage, servers, and security systems. Key back-end components are applications, services, databases, and security mechanisms that protect data.
Cloud service models build on this architecture. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources. Platform as a Service (PaaS) creates development environments. Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers ready-to-use applications.
SaaS will account for 65.9% of enterprise IT spending by 2025, up from 57.7% in 2022. About 77% of business and IT professionals use a hybrid cloud approach.
Your business needs for security, scalability, control, and budget should guide cloud model selection. Each model serves different purposes—public for cost savings and quick scaling, private for control and compliance, and hybrid for flexibility and balanced performance.
Benefits and Challenges of Moving to the Cloud

Image Source: Excellent Webworld
Cloud migration offers powerful advantages but comes with its share of challenges. A clear understanding of both aspects will help you make better decisions about your cloud trip.
Advantages of cloud computing for scalability and cost
Cloud computing’s pay-as-you-go model changes fixed costs into variable expenses. Your business pays only for services it actually uses, which eliminates heavy upfront investments in physical infrastructure. Small businesses and startups find this pricing model especially affordable.
The cost benefits go beyond hardware. Cloud providers include licensing, infrastructure maintenance, and software upgrades in their prices, which makes expenses more predictable. Companies can save substantially—over 35% on annual operating costs based on recent studies.
The exceptional flexibility of cloud scalability stands out. Resources can quickly adjust up or down based on what you need without buying new hardware. This solves capacity planning issues. Your business can handle increased volume during busy periods like sales events without any service disruptions.
Data stored in multiple locations improves disaster recovery capabilities. Your business keeps running even during unexpected outages. Systems recover almost instantly compared to traditional on-premises setups.
Common cloud computing security concerns
Storing sensitive data externally raises valid security concerns, even with strong security measures. About 45% of security incidents come from cloud environments. All but one of these companies using cloud services faced at least one data breach between 2020-2022.
Data breaches get pricey—averaging $4.88 million in 2024. These costs include direct losses, damaged reputation, and compliance penalties. The Code Space case shows how security breaches can shut down an entire business.
Limited visibility creates another security challenge. Cloud environments change often, which makes detecting threats, misconfigurations, or unauthorized access tough. Security gaps might go unnoticed without proper monitoring tools.
Different industries face strict regulatory requirements that raise compliance concerns. Companies must verify that cloud providers meet standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS to avoid legal issues.
Cloud computing drawbacks to consider
Service outages remain one of cloud computing’s biggest challenges. Downtime happens for various reasons and costs businesses around $100,000 per hour. Even industry giants like Microsoft, Google, and AWS face occasional service disruptions.
Vendor lock-in adds more complications. Moving between cloud providers becomes difficult because of proprietary technologies and complex data integration. This limits your ability to adapt to new technology or changing cost structures.
Hidden costs add up through data transfer fees, usage changes, and complex pricing plans. Only 30% of companies track their total cloud spending, which makes budget planning difficult.
Internet dependence creates another risk. Teams lose access to cloud-based applications and data without reliable connectivity. Businesses in areas with spotty internet service face operational risks because of this dependence.
Step-by-Step Guide to Cloud Migration Without the Headaches
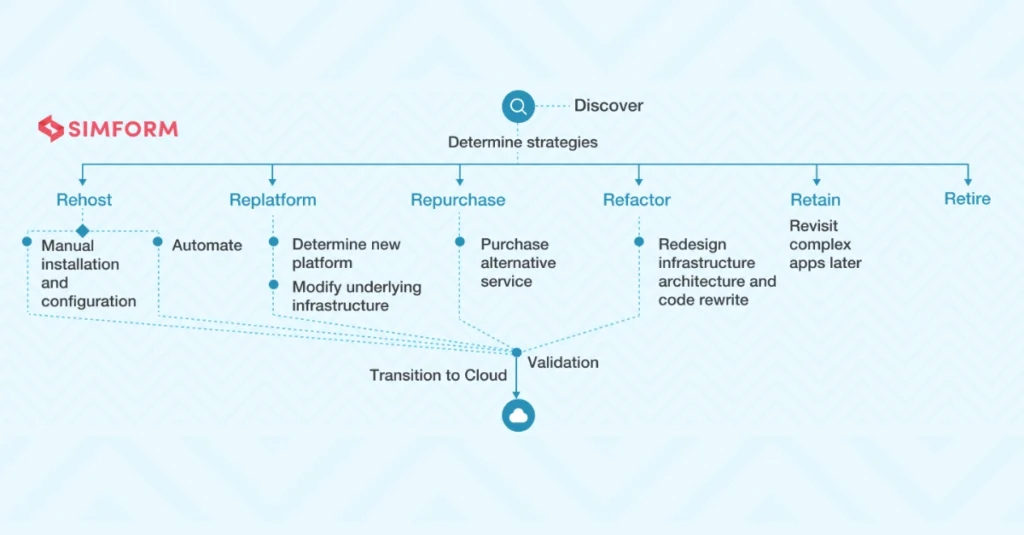
Image Source: Simform
Cloud migration success depends on good planning and execution. Here’s a breakdown of steps that will help you dodge common pitfalls.
1. Assess your current IT infrastructure
Start by creating a catalog of all your IT assets. This discovery phase typically takes several weeks to complete. List your physical machines, virtual machines, databases, and applications.
Your complete inventory should have:
- Each application’s performance needs
- How systems depend on each other
- Data sensitivity and compliance requirements
- Usage patterns
This full picture builds the foundations of your migration. You risk unexpected complications during later stages without it.
2. Choose the right cloud computing platform
Assess potential cloud providers based on:
- Their financial health and stability
- Security setup and compliance certifications
- Standard interfaces and APIs
- Support options and technical know-how
Your business needs should match the provider’s offerings. Think over their hybrid options even if they’re not in your original plan.
Meet Mehnav – we build secure, mobile-responsive websites that match your business needs. Today’s customers don’t like to wait. That’s why our websites load faster and keep users coming back.
3. Plan your data migration strategy
Look at your source data structure first. Then pick the right destination based on what you find.
Your roadmap should list:
- Timeline and resources you’ll need
- Data transfer security rules
- Backup plans for possible issues
Pick the migration strategy that fits best: rehost (lift and shift), replatform, refactor, rebuild, or replace.
4. Test and verify before full deployment
Run tests in a controlled environment before moving everything. Compare how things work against your old setup.
Your testing should include:
- Load tests to see how systems handle pressure
- Stress tests to find weak points
- Integration tests for microservice systems
Make sure everything from your old setup exists in the new one.
5. Train your team and update workflows
Cloud systems need different skills than regular ones. Training leads to success.
Figure out who does what, then create training plans that fit each role. You might want to use:
- Hands-on workshops with instructors
- Practice environments for real experience
- Cloud certification courses
Promote constant learning as cloud tech changes faster. This helps keep employees around by growing their skills and careers.
Managing Costs, Security, and Compliance Post-Migration
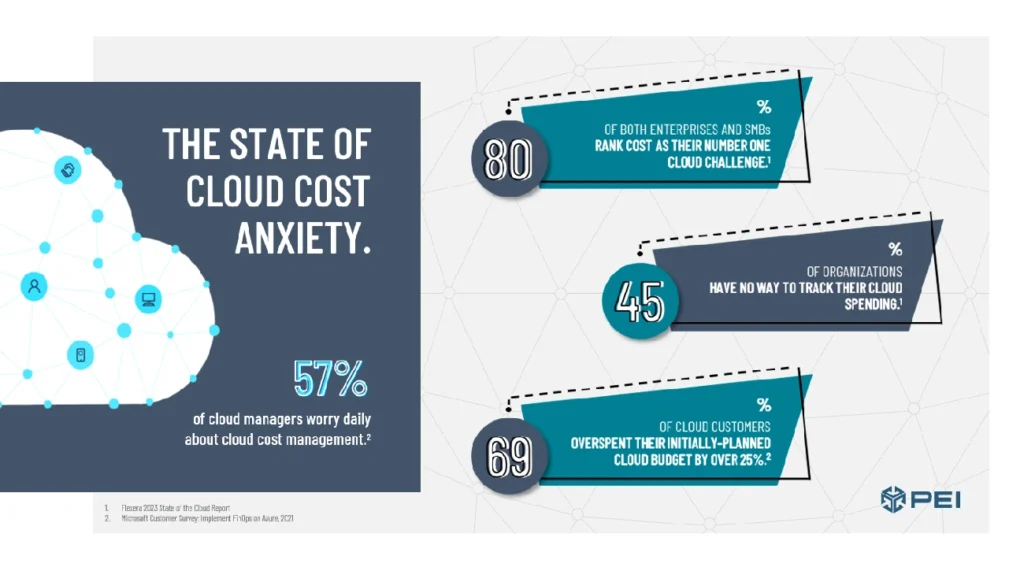
Image Source: PEI
Cloud migration success brings new priorities: managing costs, security, and compliance. These three elements need constant attention to get the most from your cloud investment.
Cloud computing cost breakdown and budgeting tips
Cloud costs can quickly spiral out of control without proper management. A cloud budget framework with clear spending limits for departments and projects should be your first step.
Your historical usage patterns will help create realistic monthly, quarterly, and yearly budgets. Here are practical strategies you can implement:
- Use resource tagging to track spending by department, project, or application
- Right-size cloud resources to eliminate waste from over-provisioned services
- Use reserved instances for predictable workloads to reduce long-term costs
- Configure cost alerts to notify stakeholders when spending approaches thresholds
- Shut down idle resources when they’re not in use
Many organizations face cost challenges after migration, such as billing surprises or inefficient resource utilization. Regular cost reviews and budget adjustments will help you stay on track.
Cloud computing security best practices
Security needs change after migration, and you need strong protection measures. Here are the main areas to focus on:
Identity and access management (IAM): Your access permissions should follow the principle of least privilege. The core team must create secure roles and implement multi-factor authentication everywhere.
Data protection: Your data needs encryption both at rest and in transit. Cloud provider services like AWS KMS help manage encryption keys effectively.
Regular security audits: You should conduct full assessments to identify vulnerabilities and maintain compliance with regulations. AWS Config and similar tools help spot insecure configurations.
CISA and NSA recommend network segmentation, secure cloud key management practices, and data protection measures. The shared responsibility model helps you understand which security aspects you control versus your provider.
Ensuring compliance with industry standards
Cloud compliance means following standards and regulations for cloud services. This protects sensitive information, ensures data privacy, and builds trust.
Your cloud provider shares compliance responsibilities with you. Many enterprises forget this fact, which can lead to regulatory fines or data breaches.
Here’s how to maintain compliance:
- Assess your specific requirements based on your data and operations
- Understand which regulations apply (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS)
- Regularly audit your cloud environment against these standards
- Review your service level agreement (SLA) to confirm it meets compliance needs
Meet Mehnav – we build fast, secure, and mobile-responsive websites that match your business needs. We know customers hate waiting, so our websites load quickly and keep your customers engaged even after cloud migration.
Conclusion
Final Thoughts on Your Cloud Trip
Businesses must embrace cloud computing to stay competitive today. You’ve learned what the cloud can do and how to pick the right model that fits your needs.
The benefits are nowhere near the challenges if you plan well. Your IT expenses can drop by 15-30%, which makes the switch worth it. It also gives you the flexibility to adapt faster to market changes.
Security risks exist, but following best practices reduces your risk by a lot. Get a full picture of your current setup before picking a provider. Create a solid migration plan and test everything properly.
Your next step is to manage costs by tagging resources and right-sizing them. Strong security measures and industry compliance will protect your data and investment. These steps are the foundations of a successful cloud setup.
Cloud computing keeps evolving faster. Your team needs regular training on new tech and developments. Success depends on both your people and technology working together.
Start now. Review your needs, check out providers, and create your plan. The cloud is a great way to get growth and breakthroughs. Your business needs these advantages to thrive in today’s digital world.



