Future of AI is evolving faster than most people think. Generative AI usage has jumped from 55% to 75% among business leaders and decision-makers. This surge shows how technology blends into our everyday lives. You might see AI as just another work tool now. But by 2025, it will become a key part of your work and personal life.
Recent AI trends show systems that think like humans do. These models use logical steps to solve complex problems, much like human reasoning. The impact goes beyond technical achievements. AI will add $4.4 trillion to the global economy each year, and that’s a big deal.
The year 2025 will change things in ways that Silicon Valley keeps quiet about. Agentic AI will work on its own to help you, while custom silicon changes how hardware works. These advances will make your life easier. This piece reveals what’s happening behind closed doors in AI labs, defense departments, and corporate boardrooms as we approach this crucial year for artificial intelligence.
The rise of agentic AI in 2025

Image Source: Siemens press
AI agents are changing everything we know about artificial intelligence. Unlike chatbots that stick to scripts, AI agents in 2025 can watch, plan, and handle complex tasks with minimal human input. These smart systems are moving fast from basic assistants to partners that make their own decisions.
From chatbots to autonomous agents
Traditional chatbots couldn’t do much beyond their programming. They followed fixed scripts and handled basic questions. AI agents work differently. They utilize state-of-the-art technologies like large language models (LLMs) to understand context, adapt to changes, and decide things on their own.
The real difference shows in what they can do. Chatbots just respond when asked. AI agents break big tasks into smaller steps, arrange work across different areas, and get better as they learn. These agents don’t stop at answering questions—they solve problems and finish entire projects without needing constant human guidance.
This rise marks a big move from reactive to proactive AI. “Technology is no longer just a tool in the cognitive era, it’s becoming an active participant in decision-making”, noted one industry expert. So companies are rushing to adopt these technologies. 99% of enterprise developers are learning about or building AI agents.
How agents are reshaping productivity
AI agents have transformed productivity. Software development teams cut their cycle times by 60% and halved their production errors. These impressive results come from agents that handle everything—from gathering requirements to writing code, testing, and fixing problems.
AI agents shine in many organizational roles:
- They find patterns in data
- They predict trends and run scenarios
- They complete tasks at scale
- They create content across media
- They suggest the best actions based on real-time context
MIT research backs these benefits. Human-AI teams showed 60% better productivity than teams with just humans. Generative AI could add between $2.60 trillion and $4.40 trillion annually to the global economy in a variety of use cases.
AI agents stand apart from older automation tools. They handle unclear situations and make their own choices, which frees humans from repetitive work. Workers can focus on strategy and creativity, extending human intelligence rather than replacing it.
Why memory and reasoning matter now
Today’s AI agents stand out because they remember and reason better. Memory helps them store and use past experiences to make better decisions. Without it, agents would forget context and learn poorly.
AI agents use several vital types of memory:
- Short-term memory keeps track of conversations
- Long-term memory saves information between sessions
- Episodic memory recalls specific experiences
- Semantic memory holds structured facts
Combined with memory, reasoning lets AI agents solve problems step-by-step like humans do. They can plan, change strategies, and complete multi-step tasks without human help. Harvey, a legal AI startup, shows this in action. Their system handles legal work from reviewing documents to predicting case outcomes.
Memory and reasoning together have brought us to what experts call “the age of AI agents.” These systems don’t just answer questions—they work toward goals for their users. We’re still at the start of what agentic AI can do. By 2029, these systems will handle 80% of common customer service issues on their own.
AI models that can reason like humans

Image Source: Datahub Analytics
AI capabilities have taken a remarkable turn with reasoning models that go beyond simple pattern matching to solve real problems. These advanced systems understand not just what you ask, but why you ask it. They can work through solutions logically, one step at a time.
What reasoning means in AI
The mechanism of AI reasoning uses available information to generate predictions, make inferences, and draw conclusions. The original preprogrammed rule systems have evolved into more flexible approaches that mirror human cognitive processes.
AI reasoning covers several distinct types:
- Deductive reasoning: Drawing certain conclusions from general principles
- Inductive reasoning: Generalizing from specific examples
- Abductive reasoning: Finding the most plausible explanation for observations
- Analogical reasoning: Transferring knowledge between similar situations
Traditional models rely on pattern recognition, but reasoning AI uses what researchers call “System 2” thinking—a considered, conscious effort applied to logical reasoning and problem-solving. This reflects the human difference between quick, instinctive responses (System 1) and methodical thinking (System 2).
Examples of step-by-step problem solving
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting stands out as one of the biggest breakthroughs in AI reasoning. Google researchers introduced this technique in 2023, which lets models tackle problems methodically by creating intermediate reasoning steps. This approach improves performance on complex mathematical and logical challenges.
Models like OpenAI’s o1 and o3 series, DeepSeek R1, Google’s Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking, and Grok 3 showcase this reasoning capability. These systems break down complex tasks into smaller parts using reasoning tokens, which enables systematic problem-solving that resembles human thinking.
Real-life applications make this difference clear. Standard models might rush to incorrect answers for complex math problems, while reasoning models take their time—13 seconds or more—to outline step-by-step solutions. This careful approach produces more accurate results.
All the same, these systems have their limits. Apple researchers published “The Illusion of Thinking,” which revealed that even advanced reasoning models struggle with highly complex problems. A key difference exists between showing reasoning-like behavior and truly grasping concepts.
Why this matters for real-life tasks
Reasoning AI’s impact reaches far beyond academic interest. Healthcare professionals can use reasoning models to analyze patient histories, symptoms, and lab results for diagnosis and treatment suggestions. These models can review different treatment paths and predict outcomes while explaining their logic for physicians to check.
Financial institutions use reasoning systems to assess complex credit risks by modeling economic scenarios. Businesses of all sizes can transform their approach to strategic planning and risk management.
Legal applications have emerged too. Reasoning AI proves contracts meet regulatory standards and documents compliance decisions. This matters because these models show their work, making them ideal for high-stakes situations that need transparency and verification.
The progress in reasoning AI looks promising, but the path to human-like reasoning continues. The goal isn’t just to copy human thought processes but to create systems that enhance human intelligence—to magnify productivity and enable breakthroughs in complex problem-solving.
AI’s growing role in science and discovery
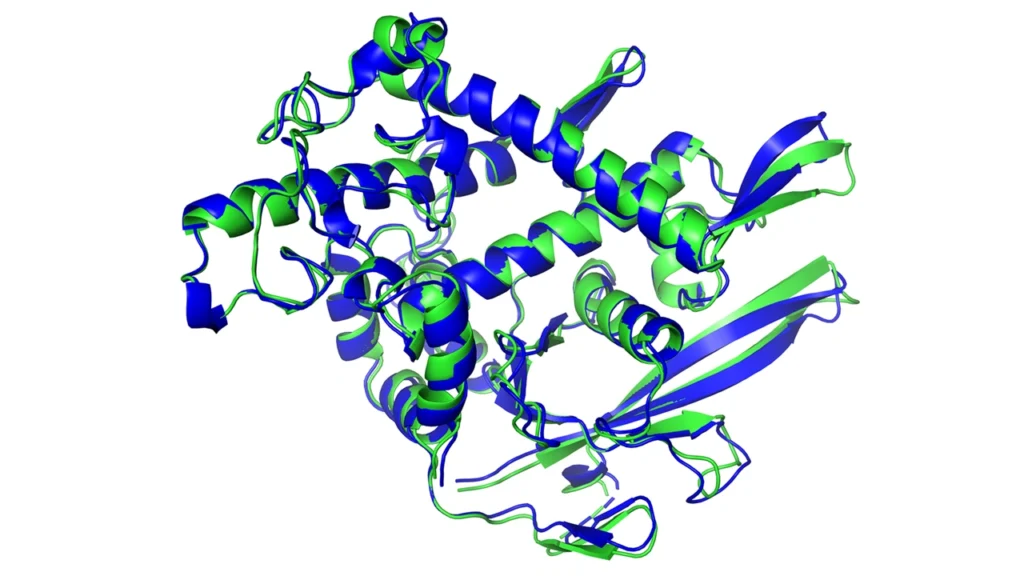
Image Source: Science
AI systems are quietly revolutionizing scientific discovery by tackling research challenges that seemed impossible before. The impact goes far beyond chatbots and personal assistants. These tools help researchers make breakthroughs that would normally take decades.
AI in biology and protein folding
Advanced AI systems have found a perfect testing ground in biological sciences. DeepMind’s AlphaFold has changed scientists’ understanding of protein structures completely. The system has predicted the three-dimensional shapes of nearly all 200 million proteins known to science. What used to take years in the lab now takes just hours of computation.
These tools have sped up our understanding of diseases and potential treatments significantly. Scientists recently used AI systems to find a new antibiotic that works against drug-resistant bacteria. The system analyzed molecular structures in ways researchers couldn’t easily notice. Pharmaceutical companies now use these protein-folding models to create targeted drugs that work better with fewer side effects.
New breakthroughs in materials science
AI-powered discovery methods have changed materials science dramatically. These systems can test thousands of potential new materials without creating them physically. This has led scientists to develop more efficient solar panels, batteries that last longer, and building materials that are stronger yet lighter.
AI systems don’t just speed up discovery – they find completely unexpected material properties. Scientists using AI algorithms found a new superconducting material that works at higher temperatures than anyone thought possible. The economic impact could be huge – these discoveries might reduce research and development cycles from 10+ years to under 3 years.
AI as a virtual research assistant
AI has become an all-purpose research assistant in scientific disciplines. These systems can:
- Find patterns in vast experimental datasets that researchers might miss
- Create and test hypotheses on their own, even operating lab equipment
- Relate thousands of research papers to keep scientists updated on new developments
Research institutions and university labs are creating custom AI assistants that understand their field’s specific vocabulary and methods. These tools don’t replace human scientists – they increase what researchers can do. The AI handles routine analysis while scientists focus on creative problem-solving and designing experiments.
Scientific discovery will likely involve teams where human intuition and AI processing power work together. This partnership could lead to breakthroughs that neither could achieve alone.
The hidden race for AI infrastructure
Image Source: NVIDIA Newsroom
A fierce competition for hardware drives the AI software revolution. This hidden race to dominate AI infrastructure reshapes global technology supply chains and creates new geopolitical flashpoints.
Custom chips and silicon wars
The race for AI supremacy has sparked an unprecedented rush to develop specialized silicon. Major tech companies now design their own custom chips instead of depending on general-purpose processors. Google led this path with its Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). Amazon, Microsoft, Meta, and OpenAI have started developing their own AI accelerators to reduce their reliance on external suppliers.
Why Nvidia is no longer alone
Nvidia currently controls between 70-95% of the AI chip market. Their dominance faces new challenges. AMD’s MI series GPUs have emerged as strong alternatives, especially after Microsoft used them for ChatGPT services. Startups like Cerebras with its trillion-transistor Wafer Scale Engine and SambaNova with its reconfigurable architecture have found success in specialized AI applications. Cloud providers have become Nvidia’s biggest customers and potential rivals. Amazon’s Inferentia chips and Google’s TPUs now power much of their internal workloads.
The geopolitics of chip manufacturing
The semiconductor supply chain shows an extraordinary risk concentration. The US, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and the Netherlands control almost all advanced chip production technology. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) makes about 68% of the world’s chips and over 90% of integrated circuits used by AI. This concentration creates a weak point for the entire AI ecosystem, especially given Taiwan’s uncertain geopolitical situation.
Energy and cooling challenges for AI data centers
AI’s computational needs create unsustainable energy requirements. Data centers use 1-2% of global electricity, matching the airline industry’s consumption. Experts predict this could double between 2022-2026 as AI adoption grows. Cooling these systems presents unique challenges. Modern GPUs generate more heat than traditional CPUs, with power densities sometimes exceeding 120kW per rack.
Want to keep up with these infrastructure challenges? Meet Mehnav, a forward-thinking website development agency that builds fast websites. The world needs speed, security, and mobile responsiveness because most traffic comes from mobile devices.
AI and national security: a quiet alliance

Image Source: U.S. Mission to the OSCE
AI has become the life-blood of modern defense strategies, transforming national security. Military establishments worldwide now accept new ideas about AI technologies to keep their strategic edge. What seemed like science fiction before has turned into reality.
Defense contracts and military AI
The Pentagon awarded OpenAI a $200 million contract to develop “prototype frontier AI capabilities” for both warfighting and enterprise domains. This partnership shows how Silicon Valley companies have started to line up with defense interests. Meta now works with defense startup Anduril to develop AI-powered combat goggles.
The Department of Defense’s 2023 Data, Analytics and Artificial Intelligence Adoption Strategy aims to “ensure U.S. warfighters maintain decision superiority on the battlefield”. Defense officials say AI-enabled systems can boost:
- Battlespace awareness and understanding
- Adaptive force planning
- Fast, precise kill chains
- Resilient support systems
Ethical dilemmas for tech companies
Tech companies face complex ethical challenges in the profitable defense sector. Many companies managed to keep policies against weapons development until now. Their employees successfully pushed back against military partnerships. Economic pressures have changed this stance. Training and running large language models costs hundreds of millions of dollars—expenses that consumer revenue alone cannot cover.
Companies have quietly changed their ethical guidelines. OpenAI removed values such as “impact-driven” from its principles and replaced them with “AGI focus”. The Pentagon’s independent weapons testing office has weakened, with staff numbers dropping from 94 to 45.
How AI is changing global power dynamics
The competition for AI superiority reshapes global power relationships. Russian President Vladimir Putin’s 2017 warning that “whoever leads in AI will rule the world” explains why major powers see AI dominance as a path to geopolitical superiority.
The US holds a substantial global advantage through tech giants like OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Nvidia. China moves faster toward its 2030 goal to become a global AI leader. The country makes use of information from its vast data pools and state-controlled initiatives. This technological race now determines future global influence.
Conclusion
The dawn of a new technological era
The AI revolution we see today could be the most important tech advancement since the internet changed our world. People often talk about consumer apps, but the real changes run deeper. By 2025, autonomous agents that can reason through complex problems will change how we use technology. These systems won’t just follow orders – they’ll know what you need and handle complicated tasks on their own.
AI does much more than just boost productivity. Research breakthroughs happen faster now with AI’s help, especially when you have complex challenges in protein folding and materials science. What used to take 20 years now takes just months or weeks.
The race for AI hardware creates both opportunities and risks. Companies fight to control the limited chip manufacturing capacity. Of course, governments see this too, which explains why tech companies and defense departments work together worldwide.
We have a long way to go, but we can build on this progress. Big questions still need answers. Can these reasoning models think like humans? Will we have enough power to run massive AI systems? Who gets to control these powerful tools?
Your future relationship with technology hangs on these answers. They’ll shape global power dynamics for decades. As AI grows stronger and more common, you need to stay informed about where it’s heading. AI’s future isn’t just about machine capabilities – it will change our world in ways we can and cannot see.


